Determining and adjusting the initial tension of PVC, PU and Silicone Conveyor Belts with textile wefts (plies)
- Conveyor Belts are designed for conveying applications.
- During initial installation, tension adjustment is essential to ensure optimum operation of your system.
- Conveyor belts are made up of textile weft and PVC or PU coating on 1 or 2 sides.
- The type of fabric (polyester, cotton, etc.), the number of plies and the belt width all influence the initial tension.
- Textile pleated belts are generally made of polyester weft (plies). The number of plies varies from 1, 2 or 3.
- The elongation tension at 1% corresponds to the value in Newton per mm of width required to elongate the belt by 1%
- Ex = 8 N/mm To elongate a belt by 1% of its length, a load of 8 Newtons per mm of width is required
- The greater the number of plies, the greater the value of 1%
| % of tension | |
|---|---|
| Width up to 1000 mm | 0.1 |
| Narrow width (- 150 mm) | 0.5 |
| Elongation at 1% greater than 15 N/mm | 0.2 |
| Elongation at 1% less than 5 N /mm | 0.4 |
Determining and adjusting the initial tension of monolithic Conveyor Belts without textile wefts (plies)
- Monolithic belts have no textile weft, only a polyurethane (PU) layer
- Elastic belts are mainly used for applications with a fixed center distance (no mechanical tensioning system).
- Shore A hardness, thickness and width have an influence on initial installation tension.
- Monolithic belts are joined endlessly according to a manufacturing dimension (length L0 at rest)
- Length L1 corresponds to the length of the belt with tension (belt under tension on the conveyor).
- To obtain the LO dimension, deduct the initial % elongation of the belt, generally referred to as pre-tensioning.
- Example: for a tensioned length of 1000 mm with an initial elongation of the belt of 5%, we obtain a manufacturing dimension of 950 mm (1000 - 5%)
- Monolithic belts are generally short, less than 10 meters
The initial tension value is expressed in %, and is generally between 0.2% and 5%
| Width 10 to 100 mm | Width 100 to 399 mm | Thickness 400 to 750 mm | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness 0.5 to 0.9 mm | 6 to 10 % | 2 to 6 % | -2 % |
| Thickness 1 to 1.9 mm | 2 to 6 % | 2 to 4 % | -1 % |
| Thickness 2 to 3 mm | Thickness 2 to 3 mm | 0.5 to 1 % | -0.5 % |
| Width 10 to 100 mm | Width 100 to 399 mm | Thickness 400 to 750 mm | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness 0.5 to 0.9 mm | 2 to 4 % | 1 to 2 % | -1 % |
| Thickness 1 to 1.9 mm | 1 to 2 % | 0.5 to 1 % | -0.5 % |
| Thickness 2 to 3 mm | 0.5 to 1 % | 0.2 to 0.5 % | -0.2 % |
The % voltages indicated are given for information only, it is necessary to make a precise calculation taking into account the load on the shaft to determine the stress on the axes or bearings.
Methodology for applying tension values
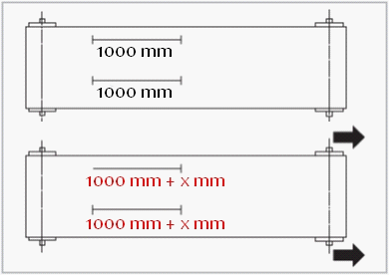
- Make a no-load mark (without tension) 1000 mm long on the belt
- Apply tension from 0.1 to 0.5 %, depending on the belt size
- Move the tension roller to lengthen the mark
- The initial mark will lengthen to 1003 mm
(for wide belts, it may be advisable to measure on both sides to avoid too great a difference in tension, which would lead to poor belt guidance).
ATTENTION :
Data and tension values are given for information only. Tanals cannot be held responsible for any misinterpretation or misuse.